AP Test: May 16th, 2024
About the AP World History: Modern Course
In AP World History: Modern, students investigate significant events, individuals, developments, and processes from 1200 to the present. Students develop and use the same skills, practices, and methods employed by historians: analyzing primary and secondary sources; developing historical arguments; making historical connections; and utilizing reasoning about comparison, causation, and continuity and change over time. The course provides six themes that students explore throughout the course in order to make connections among historical developments in different times and places: humans and the environment, cultural developments and interactions, governance, economic systems, social interactions and organization, and technology and innovation.
-Practice SPICET Theme
-Practice SPICET Theme
|
Historical Thinking Skills
|
What's in the Test?
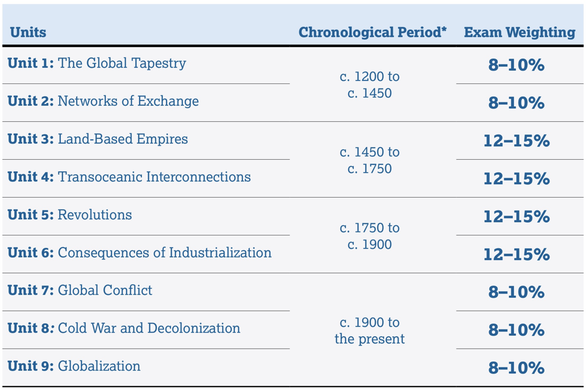
- Unit 1: The Global Tapestry You'll explore how states formed, expanded, and declined in areas of the world during the period c. 1200–c. 1450 and the related political, social, and cultural developments of that time.
- Unit 2: Networks of Exchange As you continue your study of the period c. 1200–c. 1450, you’ll learn how areas of the world were linked through trade and how these connections affected people, cultures, and environments.
- Unit 3: Land-Based Empires You'll begin your study of the period c. 1450–c. 1750 with an exploration of the empires that held power over large contiguous areas of land.
- Unit 4: Transoceanic Interconnections Continuing your study of the period c. 1450–c. 1750, you’ll learn about advances in ocean exploration, the development of new maritime empires, and the effects of new cross-cultural encounters.
- Unit 5: Revolutions You’ll start your study of the period c. 1750–c. 1900 by exploring the new political ideas and developments in technology that led to large-scale changes in governments, society, and economies.
- Unit 6: Consequences of Industrialization You'll continue to investigate the period c. 1750–c. 1900 and learn how the different states acquired and expanded control over colonies and territories.
- Unit 7: Global Conflict You'll begin your study of the period c. 1900–present by learning about the global conflicts that dominated this era.
- Unit 8: Cold War and Decolonization As you continue exploring the period c. 1900–present, you’ll learn about colonies’ pursuits of independence and the global power struggle between capitalism and communism.
- Unit 9: Globalization You'll continue your study of the period c. 1900–present by investigating the causes and effects of the unprecedented connectivity of the modern world.